Measurement Conversions
Measurement Conversions
   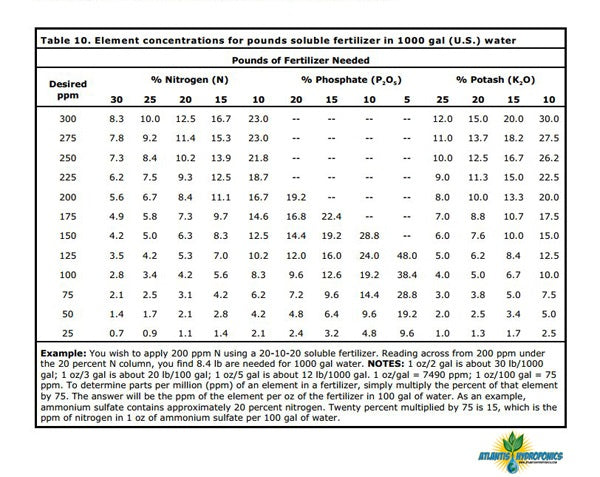        For a complete guide of conversion tables, formulas, and suggested guidelines for horticultural use, including making your own fertilizer and bulk greenhouse components, download the full PDF from the UGA Cooperative Extension, a service of the Department of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences. |
